Antidepressant Side Effect Comparison Tool
Select side effects to see personalized recommendations.
For Minimal Sexual Side Effects
Exxua (gepirone) shows the lowest rates at 2-3%, compared to 30-50% for traditional SSRIs.
For Fastest Onset
SPRAVATO (esketamine) offers relief within 24-48 hours, significantly faster than SSRIs (4-6 weeks).
For Minimal Weight Impact
Exxua shows ±0 kg weight change, while SSRIs can cause +2-5 kg.
When people hear "antidepressant" they often picture weeks of waiting for relief and a laundry list of side effects. new antidepressants are shaking up that old picture. By targeting glutamate, neurosteroids, or multiple receptors, the latest drugs aim for relief in days rather than weeks and promise far fewer issues like sexual dysfunction, weight gain, or sedation.
Quick Takeaways
- Rapid‑acting agents such as SPRAVATO and Zuranolone can improve symptoms within 24‑48 hours.
- Exxua (gepirone) shows only 2‑3 % sexual side effects versus 30‑50 % for traditional SSRIs.
- Side‑effect profiles now differ dramatically by mechanism - weight gain, dizziness, dissociation, and cardiovascular effects each cluster with specific drug classes.
- Insurance and clinic‑based monitoring remain the biggest barriers to access.
- Future tools aim to match patients to the right drug using genetics and biomarker panels.
Why Side Effects Matter So Much
Classic SSRIs and SNRIs carry a heavy burden: up to 70 % of users report sexual dysfunction, 10‑15 % see a noticeable weight gain after six months, and about half experience gastrointestinal upset. Those numbers drive drop‑out rates and push patients to seek alternatives, sometimes without medical guidance. A medication that removes or sharply reduces those unwanted effects can improve adherence, shorten depressive episodes, and ultimately lower overall health costs.
How the New Drugs Work
Understanding the mechanisms helps clinicians predict both benefits and risks.
Glutamate Modulation - SPRAVATO (Esketamine)
SPRAVATO is an NMDA‑receptor antagonist administered as a nasal spray. By dampening glutamate overactivity, it restores synaptic connections within hours. Clinical trials in JAMA Psychiatry (2023) showed a 56‑64 % bioavailability and measurable mood improvement after just 24‑48 hours.
Neurosteroid Pathway - Zuranolone
Zuranolone (brand Zurzuvae) is a positive allosteric modulator of GABA‑A receptors. A short 14‑day oral course pegs plasma levels within 1‑3 hours, delivering rapid anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. It gained FDA approval for postpartum depression in 2023 and expanded to major depressive disorder in October 2025.
Multi‑Receptor Targeting - Auvelity
Auvelity combines dextromethorphan (NMDA antagonism) with bupropion (dopamine‑norepinephrine reuptake inhibition). The combo achieves steady‑state in 4‑5 days and shows 70‑80 % oral bioavailability. Trials report a modest weight‑gain reduction compared with duloxetine.
Novel Serotonin Modulation - Exxua (Gepirone)
Exxua is the first new chemical entity for depression in over a decade (FDA approval Sep 2023). It works as a selective serotonin‑receptor partial agonist, sidestepping the classic reuptake blockade that triggers sexual dysfunction. Real‑world Reddit posts describe a near‑zero impact on libido while still lifting mood in 10‑12 days.
Psychedelic Approach - Psilocybin
Although still investigational, psilocybin received a breakthrough therapy designation in 2018 and continues to show six‑month durability after a single dose (NEJM 2024). Its mechanism involves 5‑HT2A agonism and long‑lasting neuroplastic changes.
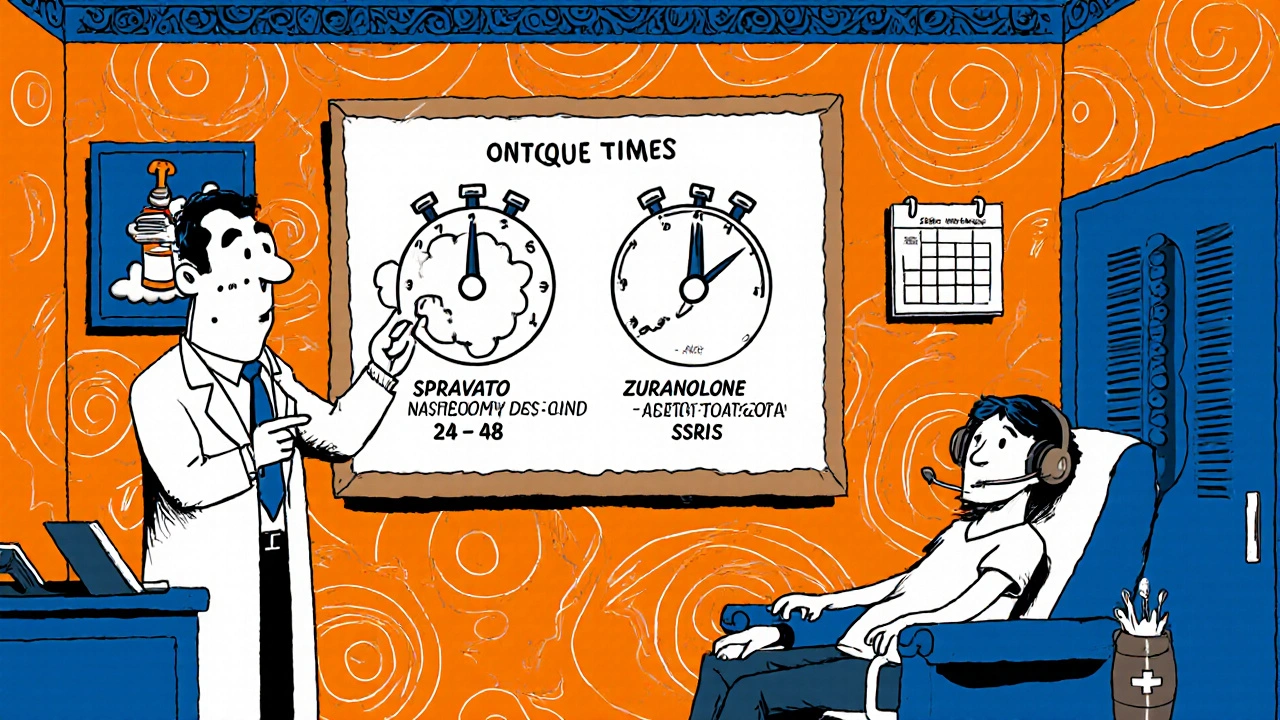
Clinical Evidence and Rapid Onset
Randomized controlled trials pooled in a Lancet review (Oct 2025) compared 151 studies of the newer agents against traditional SSRIs. Key findings:
- Response rates of 50‑65 % for rapid‑acting drugs versus 30‑40 % for SSRIs in treatment‑resistant depression.
- Onset of measurable improvement in 24‑48 hours for SPRAVATO and Zuranolone, versus 4‑6 weeks for sertraline.
- Sexual dysfunction dropped 25‑40 % across the new class, with Exxua at the low end (2‑3 %).
However, durability beyond the acute phase remains a question. SPRAVATO and Zuranolone are generally prescribed for short courses; long‑term maintenance still leans on traditional agents.
Side‑Effect Comparison
| Drug | Mechanism | Typical Onset | Sexual Dysfunction | Weight Change | Common Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exxua (gepirone) | Serotonin partial agonist | 10‑12 days | 2‑3 % | ±0 kg | Nausea, headache |
| SPRAVATO (esketamine) | NMDA antagonist | 24‑48 h | ~5 % | Minimal | Transient dissociation (45‑55 %), hypertension |
| Zuranolone | Neurosteroid GABA‑A PAM | 48‑72 h | ~8 % | ±0.5 kg | Dizziness (25 %), somnolence (20 %) |
| Auvelity (dextromethorphan/bupropion) | NMDA antagonism + DNRI | 4‑5 days | ~12 % | ±1 kg | Mild nausea, dry mouth |
| SSRIs (e.g., sertraline) | Serotonin reuptake inhibition | 4‑6 weeks | 30‑50 % | +2‑5 kg (10‑15 % gain) | Insomnia, GI upset |
| TCAs (e.g., amitriptyline) | Serotonin & norepinephrine reuptake inhibition | 3‑4 weeks | ~40 % | +3‑5 kg | Anticholinergic effects, cardiotoxicity |
Practical Considerations for Clinicians and Patients
Deciding which drug to start depends on three pillars: symptom severity, comorbid conditions, and logistics.
- Symptom urgency: If a patient is suicidal or experiences psychomotor retardation, a rapid‑acting option (SPRAVATO, Zuranolone) is usually preferred.
- Medical comorbidities: Patients with obesity or heart disease benefit from agents with minimal weight gain or cardiovascular impact (Exxua, Auvelity).
- Access & cost: SPRAVATO requires certified clinics and a 2‑hour post‑dose monitoring, creating a barrier in rural areas. Zuranolone’s 14‑day oral course is easier to dispense but carries a $9,450 price tag, far above generic SSRIs ($4 per month).
Training requirements also differ. Psychiatrists report needing 10‑15 hours of hands‑on training for SPRAVATO, while prescribing Exxua or an SSRI feels routine. Insurance prior‑authorizations are required for 92 % of commercial plans covering SPRAVATO (2025 MMIT data).
Market and Regulatory Landscape
The global antidepressant market hit $14.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow 5.2 % annually through 2030. Novel‑mechanism drugs now hold about 22 % of that market despite representing only 8 % of total prescriptions. FDA guidance released September 2025 mandates cardiovascular monitoring for all new antidepressants, a response to rising concerns about blood‑pressure spikes in older agents.
European regulators added a requirement for cognitive function testing in trial protocols (EMA 2024), nudging developers toward agents like Zuranolone that show cognitive benefits in MATRICS scores.
Key players include Johnson & Johnson (SPRAVATO), Sage Therapeutics/Biogen (Zuranolone), Axsome Therapeutics (Auvelity), and the newcomer GePirone Corp. (Exxua). Traditional manufacturers such as Pfizer and Eli Lilly continue to dominate generic SSRI sales, keeping first‑line costs low.
Future Directions
Several pipelines promise to broaden the toolbox:
- Aticaprant: A kappa‑opioid receptor antagonist in Phase 3, showing 60 % response in treatment‑resistant depression with almost no weight change.
- Genetic side‑effect profiling: NIH‑funded trials aim for 85 % accuracy in predicting sexual dysfunction or weight gain based on a patient’s DNA.
- Long‑acting formulations: Companies are exploring monthly injectable NMDA antagonists to reduce clinic visits.
As Dr. Dervla Kelly puts it, “The future isn’t a single best drug, it’s a personalized match.” The hope is that clinicians will soon have a decision‑aid that integrates genetics, comorbidities, and rapid‑onset data to pick the right agent the first time.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly can SPRAVATO improve depressive symptoms?
Most patients notice a reduction in depressive rating scores within 24‑48 hours, with peak effects around day 3.
Does Exxua cause weight gain?
Clinical data show virtually no weight change (±0 kg) in the first 8 weeks, making it a good option for patients concerned about weight.
What monitoring is required for Zuranolone?
Patients should take the tablets with food to boost absorption by about 55 % and be observed for dizziness during the first few days; no special REMS program is needed.
Are the newer antidepressants covered by insurance?
Coverage varies. SPRAVATO frequently needs prior authorization, while Exxua is often placed on a formulary tier similar to generic SSRIs. Zuranolone’s high list price leads to limited coverage, but some health plans offer patient‑assistance programs.
Can I switch from an SSRI to a rapid‑acting agent safely?
A gradual taper of the SSRI is recommended to avoid serotonin syndrome, followed by a wash‑out period (typically 5‑7 days) before starting an NMDA antagonist or neurosteroid, as outlined in the FDA’s 2025 guidance.

Katherine Brown 26.10.2025
It is noteworthy that the recent pharmacological advances strive to reconcile efficacy with tolerability, thereby addressing a longstanding therapeutic dilemma. By integrating rapid‑acting mechanisms, clinicians may now consider a broader spectrum of patient preferences without compromising safety. The emphasis on reducing sexual dysfunction and weight gain reflects an earnest response to patient‑reported outcomes, which is commendable. Moreover, the incorporation of genetic and biomarker strategies heralds a shift toward personalized psychiatry, a development that aligns with contemporary medical ethics. In sum, these innovations merit cautious optimism, provided that equitable access is safeguarded.
Ben Durham 26.10.2025
The rapid‑onset agents, particularly those modulating glutamate and neurosteroids, offer clinicians a valuable tool for acute crisis management. When evaluating these options, it is essential to consider the logistical requirements such as clinic‑based monitoring for intranasal formulations. From a pharmacogenomic perspective, emerging panels may soon guide the selection of agents like Exxua versus traditional SSRIs, minimizing adverse metabolic effects. Overall, the data suggest a pragmatic pathway to enhance adherence while mitigating common side‑effects.
Chris L 26.10.2025
This wave of novel antidepressants is truly encouraging for patients who have felt trapped by the slow‑acting nature of older drugs. The prospect of seeing mood improvement within days can restore hope and reduce the risk of dropout. It is also reassuring that many of these agents demonstrate lower rates of sexual dysfunction, which has been a major quality‑of‑life concern. While accessibility remains a hurdle, the clinical evidence supports broader adoption in treatment‑resistant cases.
Charlene Gabriel 26.10.2025
When we examine the evolution of antidepressant therapeutics, it becomes clear that we are witnessing a paradigm shift that extends far beyond simple neurotransmitter modulation. The integration of glutamate antagonism, as seen with esketamine, underscores a move toward addressing synaptic plasticity directly, which may account for the rapid symptomatic relief reported in clinical trials. Likewise, the neurosteroid pathway exploited by Zuranolone introduces a novel mechanism that harnesses the brain's innate inhibitory circuitry, offering both anxiolytic and antidepressant benefits within a remarkably short timeframe. The multi‑receptor strategy of Auvelity, combining NMDA antagonism with dopamine‑norepinephrine reuptake inhibition, exemplifies a sophisticated approach designed to balance efficacy with a more tolerable side‑effect profile. In parallel, Exxua's selective serotonin partial agonism demonstrates how nuanced receptor targeting can dramatically reduce sexual dysfunction, a side effect that has plagued patients on traditional SSRIs for decades. In addition to these pharmacodynamic advances, the field is progressively embracing precision medicine; genetic testing panels are being developed to predict individual susceptibility to adverse effects such as weight gain or cardiovascular changes, thereby enabling clinicians to customize therapy from the outset. The economic implications are also noteworthy, as the high upfront cost of agents like Zuranolone may be offset by reduced long‑term healthcare utilization due to faster remission and improved adherence. However, we must remain vigilant about the logistical challenges associated with certain treatments, such as the REMS program required for intranasal esketamine, which can limit access for patients in rural or underserved areas. The ongoing expansion of insurance coverage policies and patient assistance programs will be critical to ensure these breakthroughs are not confined to a privileged minority. Ultimately, the convergence of rapid‑acting mechanisms, favorable side‑effect profiles, and emerging biomarker‑guided prescribing heralds a new era in depression management-one that promises to be more patient‑centered, efficient, and scientifically grounded than ever before.
Leah Ackerson 26.10.2025
Ah, the lofty promises of modern psychopharmacology 🌟-they sound almost mythic, yet the undercurrents of corporate machination whisper a different tale. One might argue that the very act of branding side‑effect reduction is a clever façade, a gilded carrot to keep us obediently consuming ever‑more complex molecules. Consider how quickly we accept monitoring protocols, as if they were safeguards rather than revenue streams for clinics. In truth, the market's appetite for novelty often eclipses the humble wisdom of older, vetted therapies. 🤔
Gary Campbell 26.10.2025
Behind the glossy press releases lies a coordinated push by big pharma to monetize every nuance of neurochemistry. The rapid‑acting narrative conveniently diverts attention from the long‑term data gaps and the opaque pricing structures that burden patients. Even the FDA’s recent cardiovascular monitoring mandate feels more like a strategic concession than genuine safety enforcement.
renee granados 26.10.2025
The truth is hidden; the agencies let these drugs through to keep the money flowing.